Template Method Pattern
템플릿 메소드 패턴(Template Method Pattern)은 Gang of Four(GoF) 디자인 패턴 중
하나로 Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software 책에서 소개 된 23가지 디자인 패턴 중 하나입니다.
템플릿 메소드 패턴은 행동 패턴으로써 특정 알고리즘을 사용하는 유사한 클래스들의 알고리즘의 구조를 정의하고, 하위 클래스에서는 구조를 변경하지 않고 특정 단계 메소드들을 구체화하여 해당 구조를 표현하기 위해서 사용됩니다.
이를 통해 클라이언트는 특정 알고리즘 구조(템플릿)를 변경하지 않고 구체 메소드를 확장하거나 재정의할 수 있는 유연성을 제공합니다. 또한 정의된 구조를 제외하고 하위의 세부 실행 내용을 다양하게 구현하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
Structure
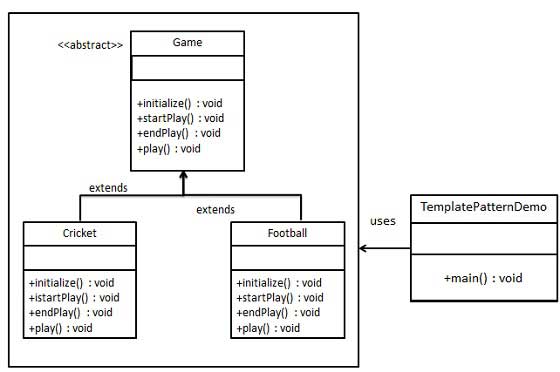
- Abstract Class
- 알고리즘의 구조를 정의하고 템플릿 메소드를 포함합니다.
- 추상 메소드와 구체 메소드를 포함하며 구체 메소드들은 템플릿 메소드를 호출하여 알고리즘의 구조를 유지합니다.
- Concrete Class
- 추상 클래스를 상속받아 템플릿 메소드를 구현하고, 필요한 구체 메소드들을 오버라이딩하여 알고리즘의 특정 단계를 구체화합니다.
Example of Template Method Pattern
JdbcTemplate
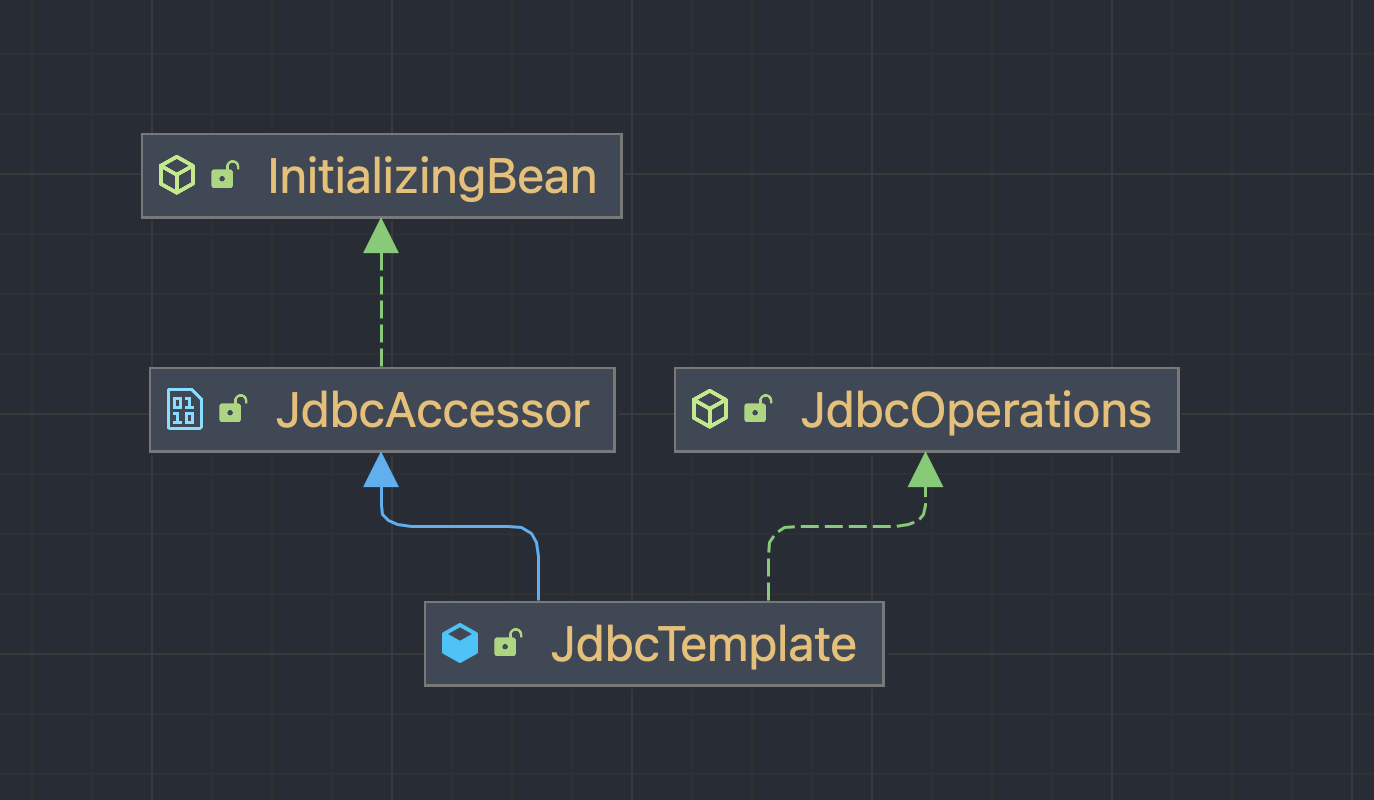
org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate은 자바에서 데이터베이스에 접속할 수 있도록 지원해주는 자바 API인 JDBC(Java Database Connectivity) 사용을 템플릿화한 클래스로 SQL 쿼리(Query) 실행이나 업데이트를 실행하고, ResultSet을 순환, 또 발생한 JDBC 예외를 잡아서 org.springframework.dao 패키지에서 정의된 일반적인 예외로 변환합니다.
또 JdbcTemplate은 템플릿 메소드 패턴과 템플릿 콜백 패턴을 적용해 구현된 클래스로 추상
클래스인 org.springframework.jdbc.support.JdbcAccessor, org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcOperations를 상속 받아 구현하였습니다.JdbcAccessor는 JDBC를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 접근하는 DAO(Database Access Object) Helper 클래스들을 위한 기본 클래스로 일반적으로 JDBC 접근 작업에 대한 데이터베이스 연결, 트랜잭션 관리, 예외 처리 등과 같은 공통된 동작을 처리하는 메소드들이 정의되어 있습니다.JdbcOperations는 JDBC 작업을 지정하는 인터페이스로 SQL 쿼리 실행, 업데이트, 프로시저 호출 등이 콜백 패턴으로 JdbcTemplate에 구현되어 있습니다.
JdbcTemplate의 경우는 템플릿 메소드 패턴에 정의되는 클래스 구조를 가지고 있지는 않지만 해당 구조를 가지는 메소드를 가지고 제한하는 점에 있어 그 기준이 부합합니다.
즉 JdbcTemplate는 구조적으로는 템플릿 메소드 패턴에 부합하진 않지만 excute() 메소드를 통해 정의한 알고리즘 구조의 변경없이 특정 알고리즘을 재정의해 사용하는 목적에 있어 템플릿 메소드 패턴을 적용한 클래스로 볼 수 있습니다.
@Override
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = con.createStatement();
applyStatementSettings(stmt);
T result = action.doInStatement(stmt);
handleWarnings(stmt);
return result;
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
// Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock
// in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet.
String sql = getSql(action);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
stmt = null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con = null;
throw translateException("StatementCallback", sql, ex);
}
finally {
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
}
}JDBC 작업을 실행하기 위한 전반적인 구조를 제공하면서, 서브클래스 또는 콜백 객체가 프로세스의 특정 부분에 대한 구체적인 구현을 제공할 수 있게 합니다.
- 데이터베이스 접속에 필요한
DataSource를JdbcAccessor로부터 획득 - 서브 클래스 또는 콜백 객체를 인자로 SQL 쿼리 실행
- 예외 처리
- 리소스 정리
위와 같이 템플릿 메소드 패턴을 활용함으로써 공통적인 JDBC 작업 흐름을 캡슐화하고 코드 재사용성을 높여 작업의 저수준 세부 사항을 걱정하지 않고 필요한 SQL 문장과 결과 추출 로직에 집중할 수 있도록 합니다.
DispatcherServlet

org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet은 HTTP 요청 핸들러/컨트롤러를 위한 중앙 디스패처로 웹 요청을 처리하기 위해 등록된 핸들러로 디스패치하며, 편리한 매핑과 예외 처리 기능을 제공합니다.
또한 DispatcherServlet은 여러 클래스들을 상속 받아 구현되었는데 그 중 org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet를 템플릿 메소드 패턴을 사용해 구현했습니다.FrameworkServlet은 processRequest()를 템플릿 메소드로 가지는데 해당 메소드 내부에 doService()가 추상 메소드로 구현되어있습니다.
즉 FrameworkServlet은 doService() 메소드에 대한 구현은 DispatcherServlet에 위임한 것입니다.
processRequest() 메소드는 doService() 메소드를 실행 시키기 전후로 특정한 알고리즘 구조를 제공합니다.
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}- 비동기 요청을 관리하는
WebAsyncManager처리를 위한CallableInterceptor를 추가합니다. LocalContext,RequestAttributes를 통해 웹 애플리케이션 컨텍스트를 초기화합니다.doService()메소드를 실행시켜 웹 요청 처리를 시작합니다.- 웹 애플리케이션 컨텍스트 홀더를 재설정합니다.
- 웹 요청 처리 결과를 로그로 남깁니다.
위와 같은 일련의 과정을 하나의 구조로 제공하며 실질적인 웹 요청 처리는 FrameworkServlet를 상속 받는 DispatcherServlet에서 구현하게 됩니다.DispatcherServlet는 doService() 또 내부적으로 doDispatch() 메소드에게 웹 요청 처리를 위임하지만 결국 해당 메소드에서 아래와 같이 로직이 수행됩니다.
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}- 요청에 대한 처리를 담당할 핸들러(컨트롤러)를 결정합니다.
- 핸들러를 실행하기 위한 핸들러 어댑터를 가져옵니다.
- 핸들러를 실행하여 요청을 처리하고, 처리 결과를 반환합니다.
- 처리된 결과를 기반으로 응답을 생성하고 전송합니다.
정리하자면 FrameworkServlet은 웹 요청 처리를 위한 템플릿 메소드로 doService()를 제공하며 하위 구현 클래스에서 해당 메소드를 구현하여 doGet(), doPost()와 같은 구체 메소드에서 해당 메소드를 실행시킵니다.
또한 DispatcherServlet은 doService() 메소드를 구현하며 핵심 웹 요청 처리 전 후처리만 외 핵심 로직은 doDispatch() 메소드에 위임하는 템플릿 메소드 패턴을 가집니다.
오탈자 및 오류 내용을 댓글 또는 메일로 알려주시면, 검토 후 조치하겠습니다.
'Software Architecture > Design Pattern' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Design] 결합도(Coupling) (0) | 2023.08.18 |
|---|---|
| [GoF] 파사드 패턴(Facade Pattern) (0) | 2023.08.17 |
| [GoF] 어댑터 패턴(Adapter Pattern) (0) | 2023.08.10 |
| [GoF] 컴포지트 패턴(Composite Pattern) (0) | 2023.07.31 |



